There are three ways to apply CSS to HTML: Inline, internal, and external.
Inline
Inline styles are put straight into the HTML tags using the
style attribute.
They look something like this:
Internal
Embedded, or internal, styles are used for the whole page.
Inside the head element, the style tags surround all of the styles for the page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Example</title>
<style>
p {
color: red;
}
a {
color: blue;
}
</style>
...
This will make all of the paragraphs in the page red and all of the links blue.e="color: red">text</p>
Simple CSS page
External
Inside the head element, the style tags surround all of the styles for the page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Example</title>
<style>
p {
color: red;
}
a {
color: blue;
}
</style>
...
This will make all of the paragraphs in the page red and all of the links blue.e="color: red">text</p>
External
External styles are used for the whole, multiple-page website. There is a separate CSS file, which will
simply look something like:
p {
color: red;
}
a {
color: blue;
}
If this file is saved as “style.css” in the same directory as your HTML page then it can be linked to in
the HTML like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Example</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
CSS has selectors. Selectors are the names given to styles in internal and external style sheets.
A value is given to the property following a colon. Semi-colons are used to separate the properties.
body {
font-size: 14px;
color: navy;
}
This will apply the given values to the font-size and color properties to the body selector.
CSS Syntax
A CSS rule-set consists of a selector and a declaration block:
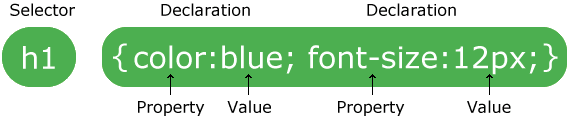
The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
A CSS declaration always ends with a semicolon, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces.
In the following example all <p> elements will be center-aligned, with a red text color:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><style>
p {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
</style></head><body>
<p>Hello World!</p>
<p>These paragraphs are styled with CSS.</p>
</body>
</html>
The id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML element to select a specific element.
The id of an element should be unique within a page, so the id selector is used to select one unique element!
To select an element with a specific id, write a hash (#) character, followed by the id of the element.
The style rule below will be applied to the HTML element with id="para1":
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#para1 {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="para1">Hello World!</p>
<p>This paragraph is not affected by the style.</p>
</body>
</html>
The class selector selects elements with a specific class attribute.
To select elements with a specific class, write a period (.) character, followed by the name of the class.
In the example below, all HTML elements with class="center" will be red and center-aligned:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.center {
text-align: center;
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="center">Red and center-aligned heading</h1>
<p class="center">Red and center-aligned paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
No comments:
Post a Comment